RANKL Reporter HEK 293 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ RANKL Cells Human & Mouse RANKL Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-ranklv2
|
|||
|
HEK-Blue™ RANKL vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-ranklv2-av
|
![]() Cytokine offer: For each cytokine reporter cell line purchased, get a free vial of the matching cytokine. View all InvivoGen's Cytokine Bioassays.
Cytokine offer: For each cytokine reporter cell line purchased, get a free vial of the matching cytokine. View all InvivoGen's Cytokine Bioassays.
RANKL-responsive NF-κB-SEAP reporter cells
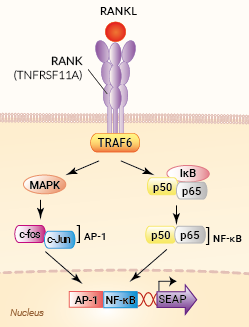
Signaling pathways in HEK-Blue™ RANKL cells
HEK-Blue™ RANKL cells are designed to monitor human RANKL-induced NF-κB/AP-1 stimulation or inhibition through SEAP detection. This colorimetric bioassay can be used for screening activatory molecules, such as engineered cytokines, or inhibitory molecules, such as neutralizing antibodies.
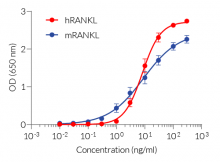
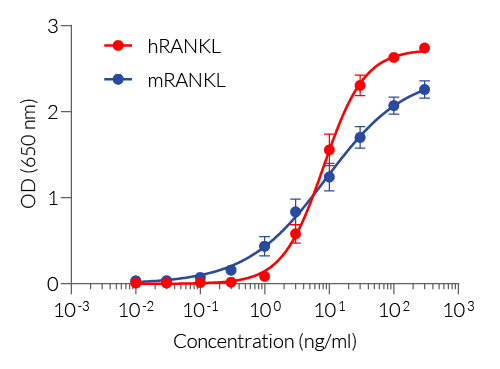
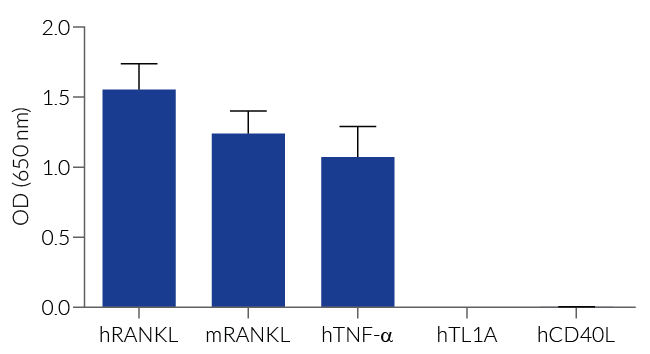
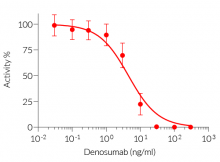
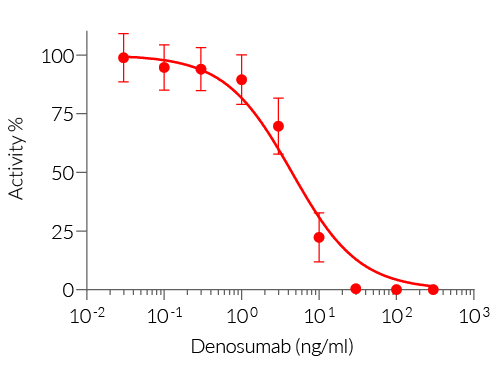
HEK-Blue™ RANKL cells respond specifically to recombinant human RANKL. The reliable and consistent performance of HEK-Blue™ RANKL cells makes them suitable for release assays of therapeutic molecules that inhibit RANKL signaling, such as Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody blocking the interaction between RANKL and its receptor RANK (see figures).
Key features
- Readily assessable NF-κB/AP1-inducible SEAP reporter activity
- Convenient readout using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution
- Strong response to human (h) and mouse(m) RANKL
- Stability guaranteed for 20 passages
Applications
- Therapeutic development
- Drug screening
- Release assay
Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand (RANKL) is a member of the TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) superfamily. This cytokine exists as a soluble or transmembrane protein produced by osteoblasts and activated T cells. RANKL binding to its receptor RANK and the subsequent signaling events play a pivotal role in bone remodeling and dendritic cell survival, thereby enhancing the induction of T cell responses. Blocking the binding of RANKL to its receptor RANK has been shown to reduce osteoporosis, prevent skeletal-related events (SREs) from bone metastasis in cancer, or improve anti-tumor immunity.
Note: A new clone is provided with an improved RANKL response. The cat code has been changed accordingly (hkb-ranklv2).
Back to the topSpecifications
Cell type: Epithelial
Tissue origin: Human Embryonic Kidney
Target: RANKL
Specificity: Human, mouse
Reporter gene: SEAP
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Zeocin®
Detection ranges:
- Human RANKL: 3 - 100 ng/ml
- Mouse RANKL: 1 - 100 ng/ml
Growth medium: Complete DMEM (see TDS)
Growth properties: Adherent
Mycoplasma-free: Verified using Plasmotest™
Quality control: Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
Back to the topContents
HEK-Blue™ RANKL Cells (hkb-ranklv2)
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
HEK-Blue™ RANKL vial (hkb-ranklv2-av)
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Notification: Reference #hkb-rankl-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-rankl.
Back to the topDetails
Cell line description
HEK-Blue™ RANKL cells were generated by stable transfection with the gene encoding for human RANK (with all three functional TRAF-binding motifs) and an NF-κB/AP1-inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter. The binding of RANKL to its receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to the activation of NF-κB/AP1, and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
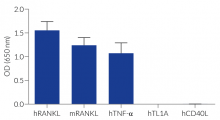
HEK-Blue™ RANKL cells respond to human (h) and mouse (m) RANKL. They can also be used for screening and release assay of molecules that inhibit RANKL signaling, such as denosumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting RANKL. Of note, these cells respond to hTNF-α. They do not respond to hTL1A or hCD40L (see figures).
RANKL background
Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand (RANKL), also known as member 11 of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily (TNFSF11) or TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE), exists as a transmembrane or soluble protein produced by osteoblasts and activated T cells [1]. RANKL binds to its receptor RANK via an obligate trimer configuration [1, 2].
RANKL/RANK signaling plays a pivotal role in bone remodeling and dendritic cell survival, thereby enhancing the induction of T cell responses [1]. Upon RANKL binding, RANK trimers recruit TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) adaptor proteins, such as TRAF6, to TRAF-binding motifs within their cytoplasmic domains [1].
The TRAF6 signaling cascade results in the activation of NF-κB and AP-1 transcription factors. Multiple efforts have focused on the development of anti‑RANKL antibodies or small‑molecule inhibitors for blocking RANKL/RANK signaling to reduce osteoporosis, prevent skeletal-related events (SREs) from bone metastasis in cancer, or improve anti-tumor immunity [1-3].
1. Cheng ML. & Fong L., 2014. Effects of RANKL-targeted therapy in immunity and cancer. Front. Oncol. 3:329.
2. Ahern E. et al., 2018. Roles of the RANKL-RANK axis in anti-tumour immunity — implications for therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15:676-93.
3. Nakai Y. et al., 2019. Efficacy of an orally active small-molecule inhibitor of RANKL in bone metastasis. Bone Res. 7:1.